Medicinal plants A|B|C
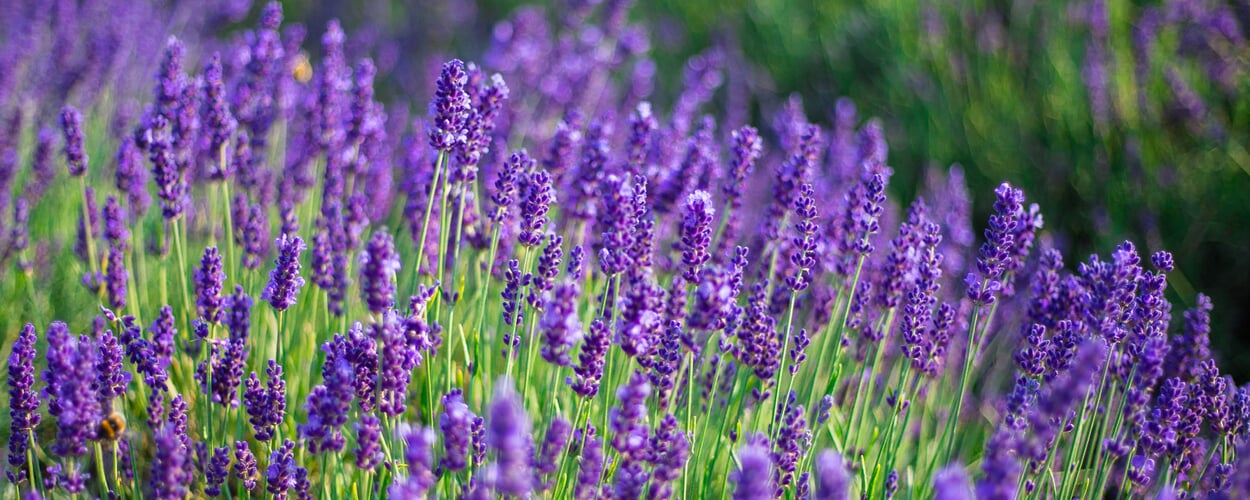
Lavender (Lavandula spec.)
All lavender species grow as half-shrubs, so they lignify in their lower parts and sprout anew from them every year. Green lavender (L. angustifolia) grows to about half a meter tall; its narrow leaves, when young, are covered with white-felty hairs to protect against excessive evaporation. Lavandin (L. intermedia) is a natural cross between true lavender and spike lavender; as a hybrid plant, it cannot reproduce by seed and must be propagated by cuttings.
Origin and cultivation.
True lavender comes from the hot and dry mountain coasts of the western Mediterranean. The vast lavender fields that bathe Provence in deep blue from June to August are not usually made of true lavender, however, but of lavandin. The latter also thrives in the lowlands, grows much taller than true lavender and its flowers produce a much higher yield of essential oil. True lavender, on the other hand, can only be grown above 800 meters. The quality of its oil increases with the altitude of the growing region; wild collections from as high as 1,800 meters fetch the highest prices.
Ingredients.
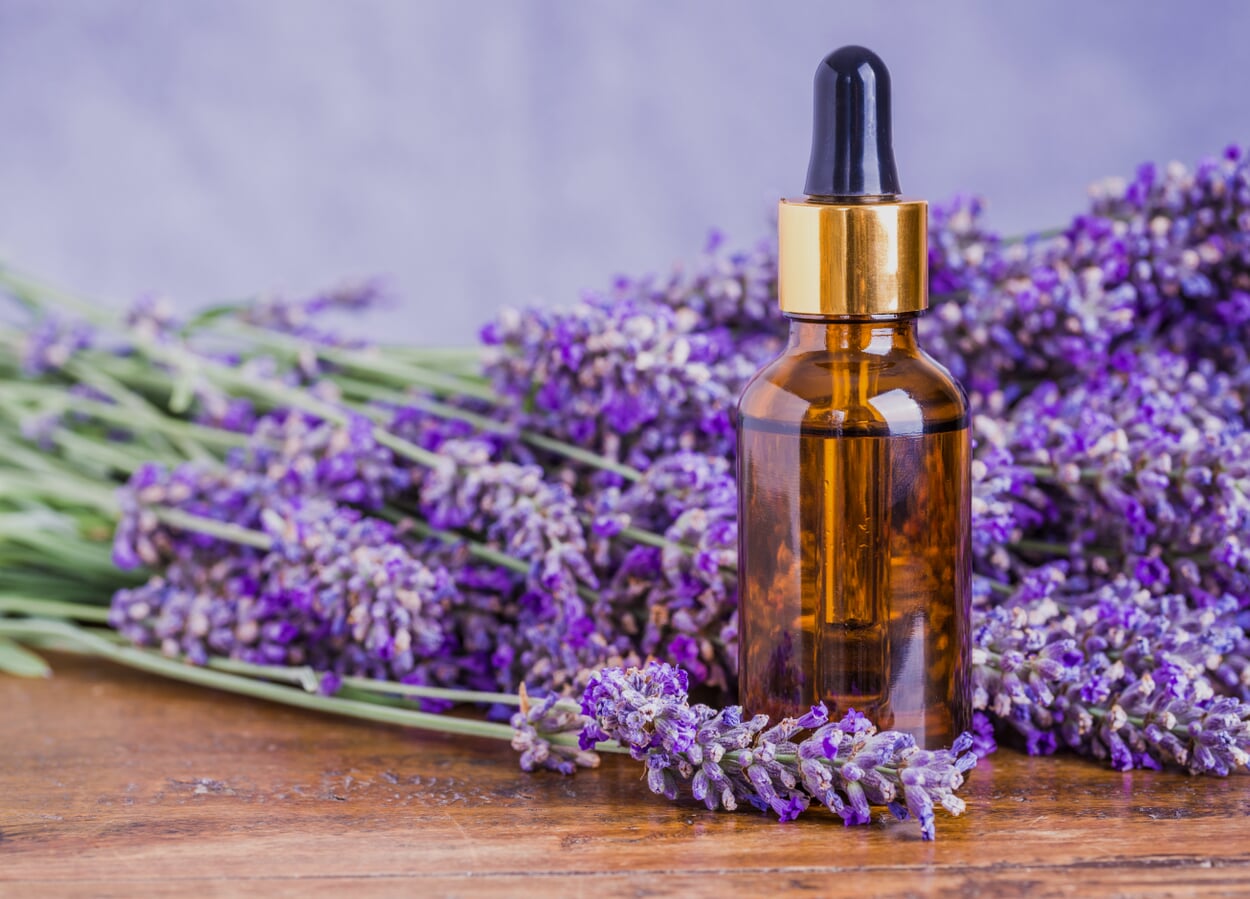
All parts of the lavender plant contain essential oil, but the highest concentration is found in the flowers. At least 150 kilograms of flower panicles of the true lavender are needed to obtain one kilogram of lavender oil by distillation (lavandin: 35 kilograms). Lavender water remains as a by-product of the distillation process. The essential oil obtained from lavandin smells more intense than that of true lavender and is used mainly as a fragrance. Thanks to its camphor content, it has an invigorating rather than a calming effect. For medicinal use, only the oil of true lavender is considered, which does not contain camphor.
Products with lavender oil
Use of the lavender.
- True lavender is a proven panacea that has a decongestant, relaxing, germicidal and anti-inflammatory effect. Its relaxing and balancing effect is used for sleep disorders as well as headaches and migraines
- Just like the essential oil of true lavender, its lavender water has a calming effect
- Lavender oil has proven analgesic effects and can be applied undiluted for toothaches, earaches and headaches. It can also be used locally for insect bites, burns and scalds.
- Lavandin ("cleaning lavender") is used as a fragrance in soaps and other cosmetics, but it also performs well in the home, for example in cleaning products. Its particularly intense odor drives away moths, which is why the Romans already put dried lavender flowers between their laundry.
Lavender oil is one of the few essential oils that can be applied undiluted to the skin.
Exclusive Manufactum body care products
Recommended Topics
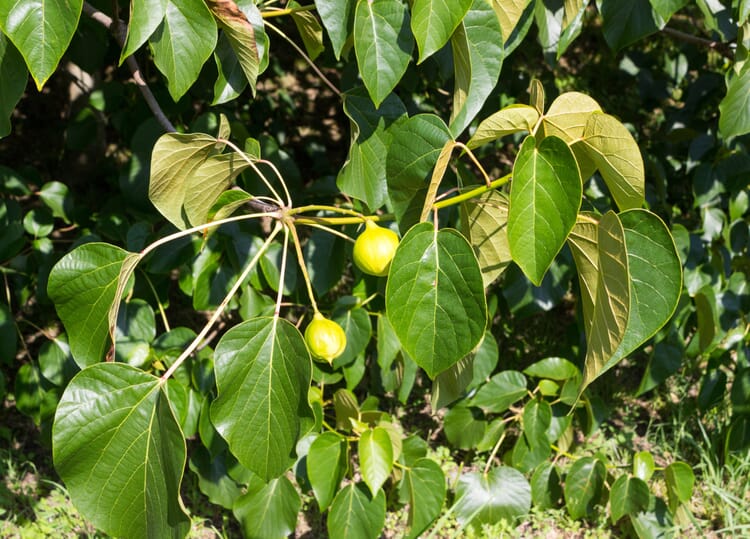
The shea tree, also known as the shea nut tree, grows up to 15 meters high; on the poor soils of its homeland, it usually grows as a solitary tree. The tree does not begin to blossom until it is about 20 years old, and its full yield is reached at the age of 50. The edible berry fruits grow in clusters at the ends of the branches; each fruit contains a seed about four centimeters in size, the shea nut. For a long time, only women were allowed to pick up the fruit and process the seeds after removing the pulp.
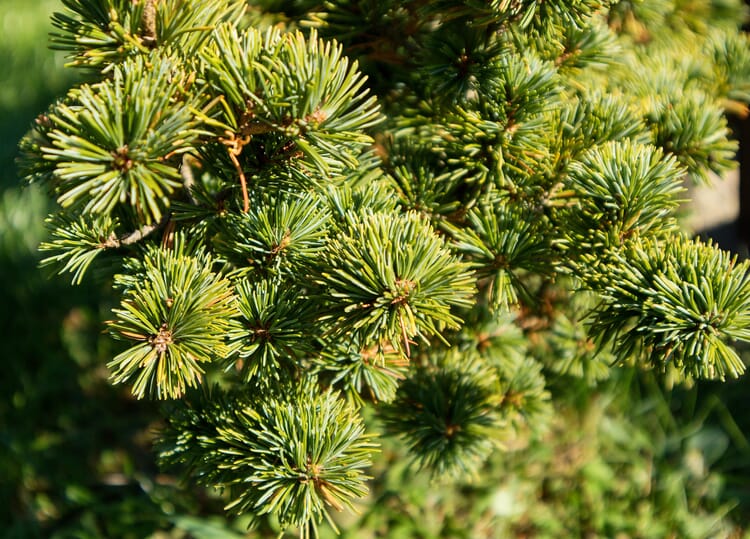
View moreAlso known as mountain pine, the tree grows to a height of about ten meters and can withstand extreme site conditions: long, snowy winters, strong winds and very dry but also very moist soils. With their widely branched, shallow root system, mountain pines persist even in stony steep slopes, where they serve as important avalanche protection. Specimens near the tree line often belong to a particular subspecies: As a low-lying shrub-like growing "lodgepole pine" it sometimes grows only one meter high.
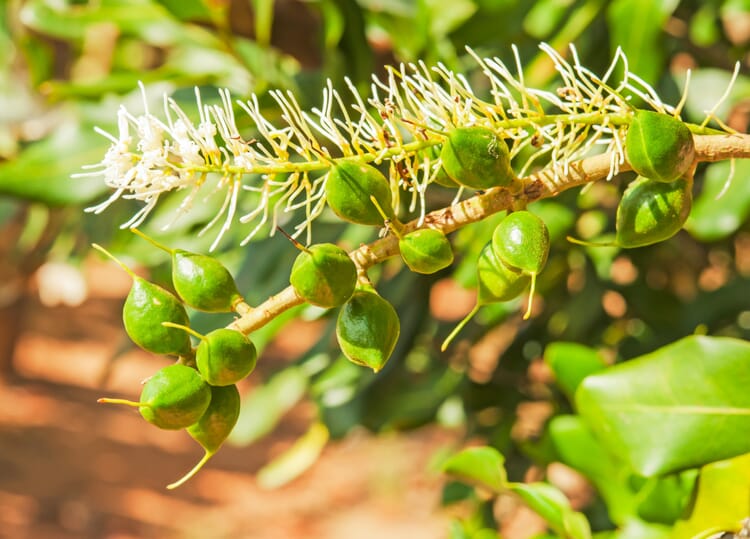
View moreThe plant genus was discovered in the 19th century by the then director of the Melbourne Botanic Garden on one of his many expeditions; he named it after his friend John McAdam. Macadamia trees grow up to 15 meters high. About a dozen spherical, green fruits each ripen on pendulous flower panicles; when they burst open, the nuts fall to the ground. Macadamia nuts in the trade mostly come from the species M. integrifolia and M. tetraphylla and their crosses.
View more