- Aloe vera
- Apricot
- Argan tree
- Arnica
- Avocado
- Bay rum tree
- Bergamot orange
- Birch
- Carnauba Palm
- German Chamomile
- Bay laurel
- Common Sage
- Eucalyptus
- Fennel
- Norway spruce
- Clove tree
- Common Nettle
- Hops
- Magnolia
- Iceland moss
- Jojoba
- Coffee tree
- Cacao tree
- Camphor tree
- Shea tree
- Mountain pine
- Lavender
- Macadamia
- Almond Tree
- Lemon balm
- Myrrh
- Olive tree
- Orange tree
- Peppermint
- Calendula
- Rose
- Horse chestnut
- Soybean
- Tea tree
- Black cohosh
- Witch hazel
- Rowanberry
- Castor oil plant
- Lemon
Medicinal plants A|B|C
Argan tree (Argania spinosa)
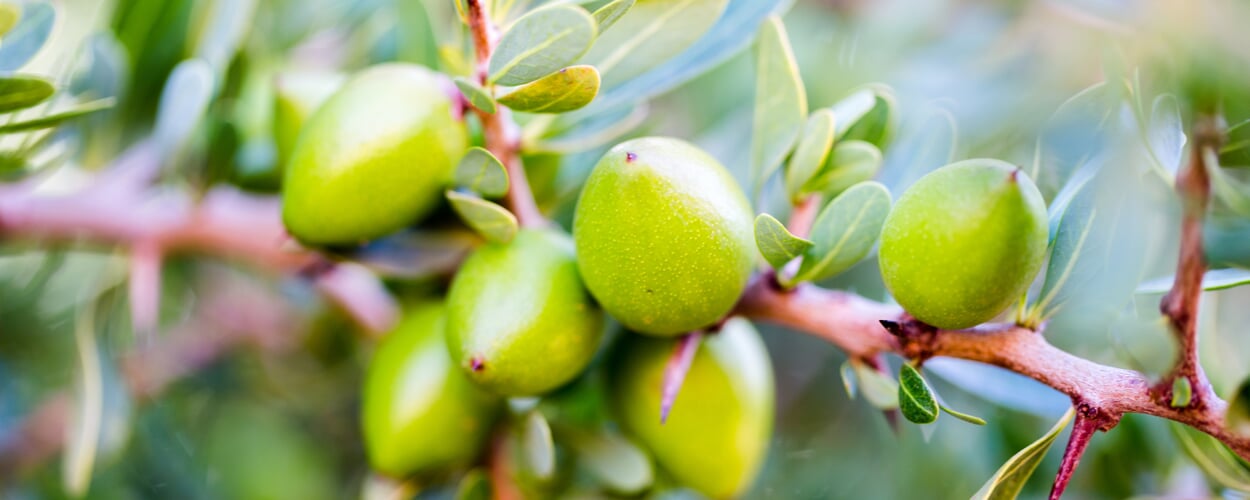


The wide spreading branches of the argan tree, which grows up to twelve meters high and is native to the semi-desert, provide shade for humans and animals. Every two years, and only when there is no dry period, the argan tree produces yellowish fruits. They are barely the size of a plum and have a bitter pulp that is inedible to humans. An extremely hard shell encloses the fruit core and protects the two to three seeds inside, from which the precious argan oil is extracted.
Origin and cultivation
Originally, the argan tree was widespread throughout much of North Africa and southern Europe, but today it is found alone in a protected area of only about 8,200 km2 in southwestern Morocco. Each argan tree is officially the property of the Moroccan state, but the use of the trees is left to the resident Berber families. Due to the high demand for argan oil, there are intensive efforts to reintroduce argan trees in countries with suitable climates, for example in Israel and in Saudi Arabia. But so far, they only reach maturity and fruitfulness in Morocco.
Ingredients
Argan oil is golden yellow and smells intensely nutty. It has a high content of essential unsaturated fatty acids. The substance group of antioxidant tocopherols (vitamin E) is also present in unusually high concentrations: Compared to olive oil, argan oil contains almost twice the amount. Also certain phytosterols, which occur only very rarely in other vegetable oils, are contained in argan oil in a unique composition and unfold caring effects for skin and hair. Ingredients that have a mild disinfectant effect and stimulate the metabolism complete the spectrum of action.
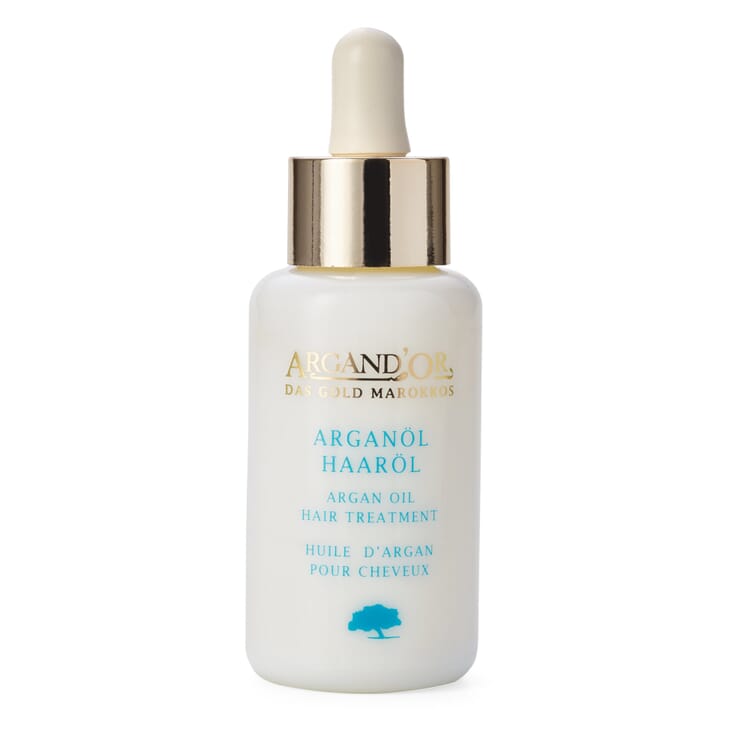
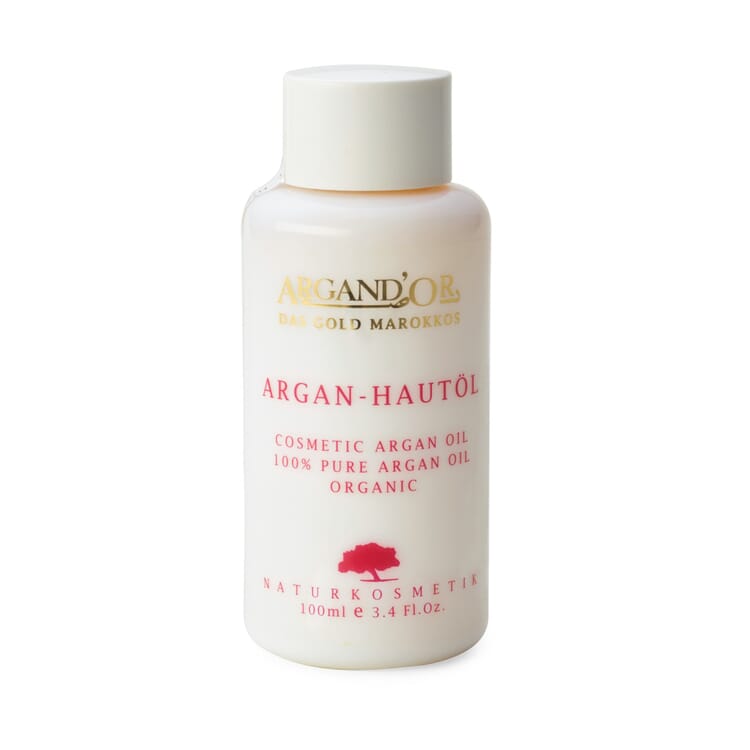
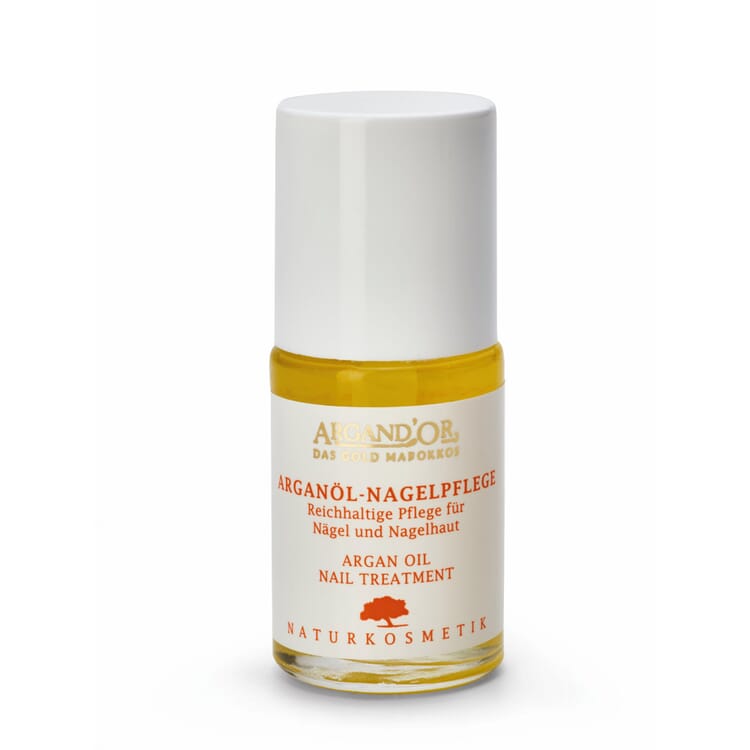
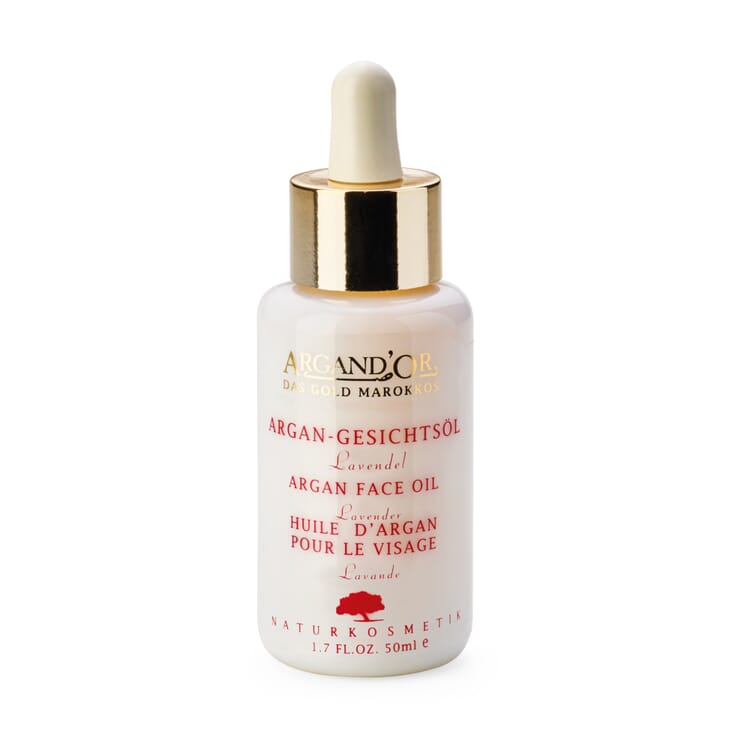
Products with argan oil
Use of argan oil
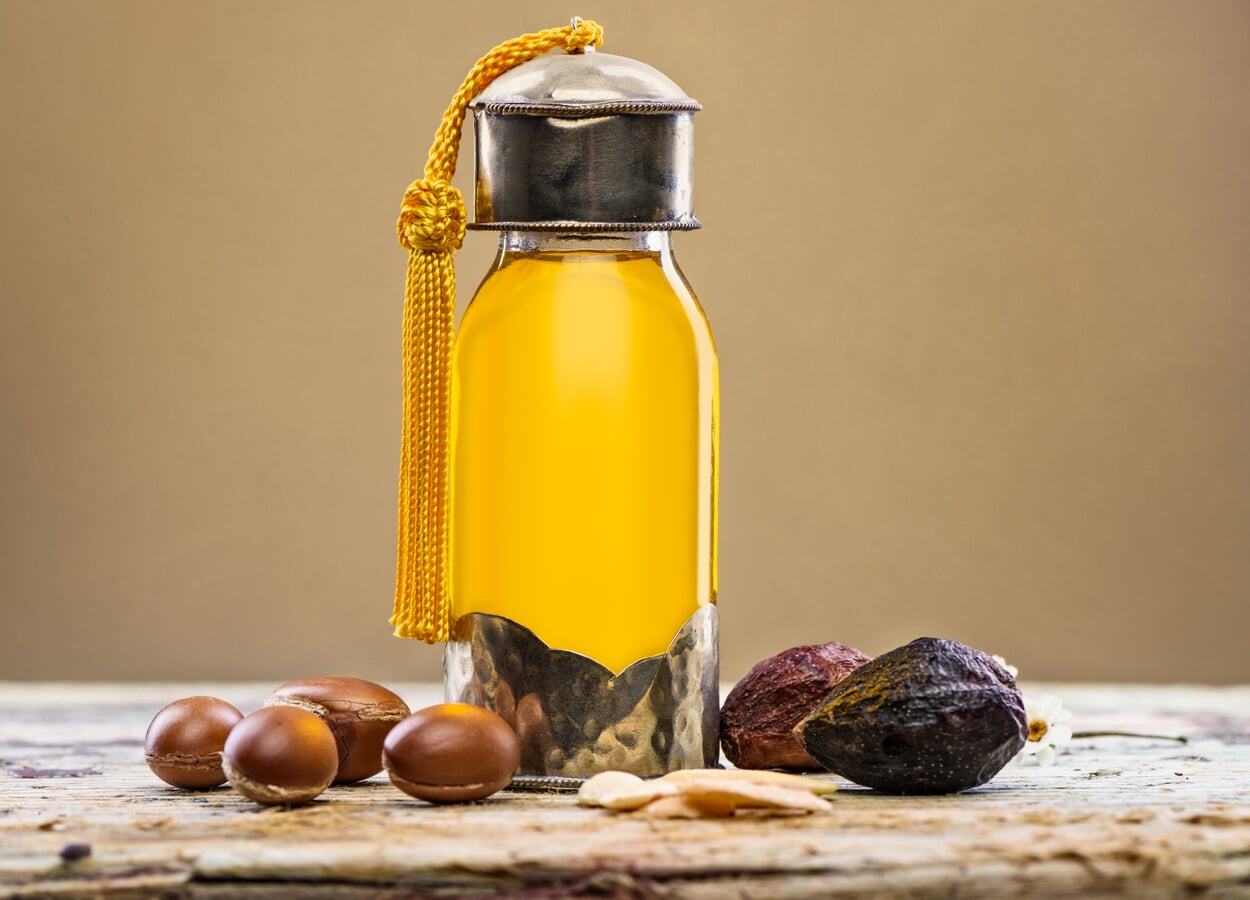


- In Moroccan cuisine, argan oil - obtained from roasted kernels and therefore with a particularly intense aroma - is served with bread and couscous. In this country, it is mostly used to refine salads, vegetables, meat and fish
- for cosmetic purposes, milder argan oil from unroasted kernels is used. Traditionally, it cares for stressed skin and helps with skin diseases such as eczema, psoriasis and sunburn. For this purpose, it is massaged into the skin pure or also mixed with almond oil, for example
- Treatment of inflammatory acne can also be successful with argan oil, because it calms the excessive skin fat production without clogging the skin pores.
To obtain one liter of argan oil, 30 kilograms of fruit are processed - the equivalent of harvesting a full-grown argan tree. In addition, its production is very labor-intensive. This makes argan oil an extraordinarily valuable food and cosmetic, with a price per liter at times exceeding 100 euros.
Exclusive Manufactum body care products
Recommended Topics
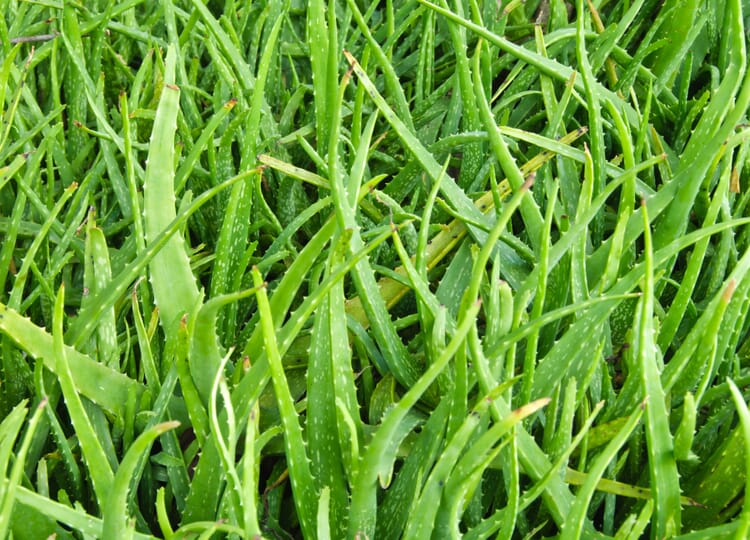


Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis) belongs to the asphodel family, so it is more closely related to torch lilies and steppe candles than to agaves. Its toothed leaves, up to 90 centimeters long, stand in rosettes and are fleshy thickened. In the flowering season, a branched flower stalk up to three meters high grows up from the gray-green rosette, densely covered at its ends with yellow or red individual flowers, depending on the variety.
View more
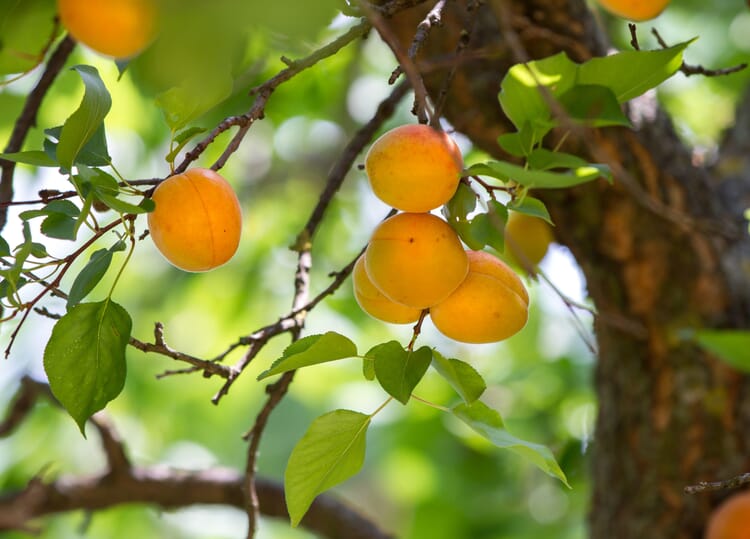

The apricot (Prunus armeniaca), also called apricot in Austria and Bavaria, grows in tree or shrub form. The yellow to orange fruits have a smooth, almost hairless surface. If the wrinkled stone of the apricot, which is pointed on one side, is cracked, the seed ("kernel") inside is revealed. It is about the size of a thumbnail and contains a lot of oil. As with almonds, there is a bitter and a sweet form. Valuable apricot kernel oil is obtained from both varieties.
View more
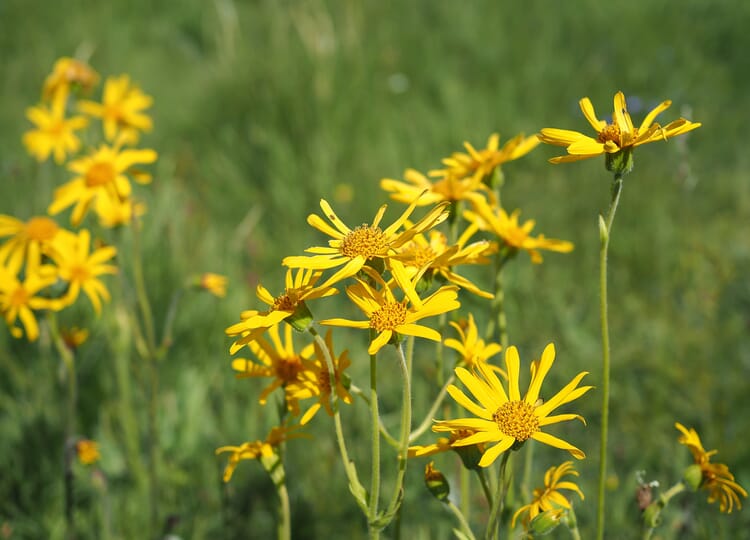

The sunny yellow, almost palm-sized flowers of arnica appear from June to August and have the typical structure of a composite flower. The whole plant has glandular hairs and smells aromatic. Originally it was at home everywhere in Europe, Central Asia and North America on nutrient-poor (mountain) meadows and boggy sites. But because there are hardly any unfertilized areas left and arnica was intensively collected for centuries because of its healing power, it has become very rare.
View more